Understanding Torn Meniscus

Imagine your knee as a complex machine with various parts working together. One of these important parts is the meniscus, a C-shaped piece of cartilage that acts as a shock absorber and cushions your knee joint. A torn meniscus is a common injury that occurs when this cartilage tears, leading to pain, swelling, and difficulty in moving your knee.
Anatomy of the Meniscus and its Role in Knee Function
The meniscus is a crucial component of your knee joint, playing a vital role in maintaining its stability and function. It acts as a shock absorber, distributing forces across the joint and preventing excessive wear and tear on the cartilage. The meniscus also helps to maintain the shape of the knee joint, allowing for smooth movement and preventing the bones from rubbing against each other. There are two menisci in each knee: the medial meniscus on the inner side of the knee and the lateral meniscus on the outer side.
Types of Meniscus Tears and their Causes
Meniscus tears can occur in various ways, resulting in different types of tears. The most common types of meniscus tears include:
- Horizontal Tear: This type of tear occurs across the width of the meniscus, often due to a twisting injury or a sudden impact.
- Vertical Tear: This tear runs from the top to the bottom of the meniscus, commonly caused by a sudden force or impact.
- Radial Tear: This tear resembles a spoke in a wheel, extending from the outer edge of the meniscus towards the center.
- Degenerative Tear: This type of tear occurs over time due to wear and tear, often affecting older individuals.
Activities that Commonly Lead to Meniscus Tears
Meniscus tears are often caused by sudden movements or impacts that put stress on the knee joint. Here are some activities that commonly lead to meniscus tears:
- Sports: Activities like basketball, football, soccer, and skiing involve sudden changes in direction, twisting movements, and impacts, increasing the risk of meniscus tears.
- Lifting Heavy Objects: Improper lifting techniques can put significant stress on the knee joint, leading to meniscus tears.
- Falls: Falling directly onto the knee can cause a sudden impact that tears the meniscus.
- Twisting Movements: Sudden twisting movements, such as those experienced during sports or daily activities, can put pressure on the meniscus and cause a tear.
Prevalence of Meniscus Tears in Different Age Groups and Demographics
Meniscus tears are a common injury that can affect individuals of all ages and demographics. However, certain factors can increase the risk of developing a torn meniscus. For example, athletes, especially those involved in high-impact sports, are at a higher risk of experiencing a meniscus tear. Additionally, older individuals are more susceptible to degenerative meniscus tears due to wear and tear on the cartilage.
According to a study published in the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, the prevalence of meniscus tears is estimated to be around 70% in individuals over the age of 65.
Torn Meniscus Recovery
/arthroscopy_torn_meniscus-65041641b6c14e0b8dd07c1f0ea6d9a7.jpg)
Torn meniscus recovery can be a journey, but with the right approach, you can get back to your active lifestyle. There are various treatment options available, and choosing the right one depends on your specific situation. Let’s explore them.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Non-surgical treatments are often the first line of defense for a torn meniscus. These options aim to reduce pain and inflammation while allowing the injury to heal naturally.
Here’s a rundown of common non-surgical treatments:
- RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation): This classic approach helps reduce swelling and pain. Resting the injured knee, applying ice packs, compressing the area, and elevating the leg can significantly improve comfort and promote healing.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen the muscles surrounding your knee, improve flexibility, and enhance joint stability. This helps regain mobility and prevent further injury.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and inflammation. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger pain medications or anti-inflammatory drugs.
While non-surgical treatments are effective for many people, they have limitations. They might not be suitable for all types of meniscus tears, especially those involving significant damage or instability. Additionally, recovery time can vary depending on the severity of the tear and individual factors.
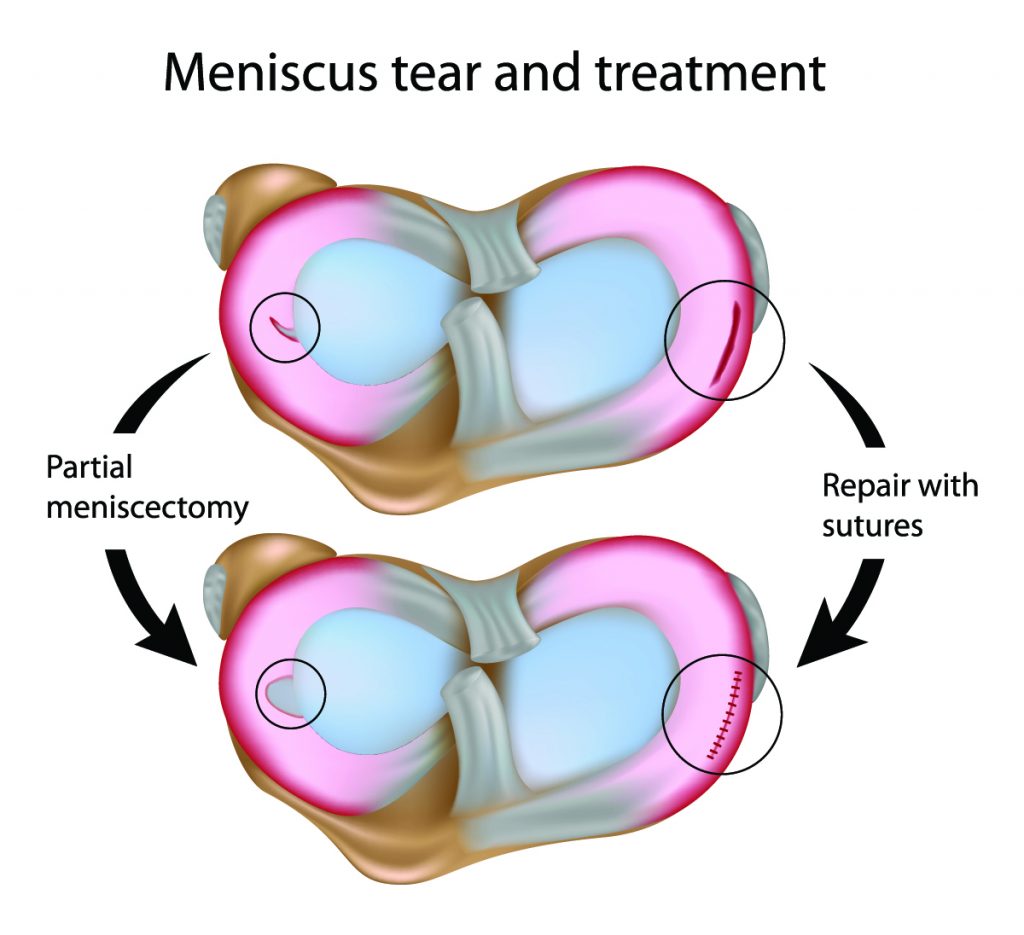
Surgical Treatment Options
For more severe meniscus tears, surgery might be necessary. There are two main types of surgical procedures:
- Meniscus Repair: This procedure involves stitching the torn meniscus back together. It’s often considered for younger individuals with a healthy meniscus and a relatively small tear. Repairing the meniscus helps preserve the natural shock-absorbing function of the knee joint.
- Meniscectomy: This involves removing the damaged portion of the meniscus. It’s typically performed for older individuals with larger tears or when the meniscus is too damaged to repair. While meniscectomy can relieve pain and improve function, it can lead to long-term joint degeneration.
The choice between repair and removal depends on various factors, including age, activity level, the extent of the tear, and the overall health of the knee.
Treatment Options Comparison
Here’s a table summarizing the pros and cons of each treatment option:
| Treatment Option | Pros | Cons | Recovery Time | Potential Complications | Long-Term Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Surgical Treatment (RICE, Physical Therapy, Medications) | Minimally invasive, less risk of complications, potential for natural healing | May not be effective for all tear types, longer recovery time, may not fully address pain and instability | 6-8 weeks | Limited, usually related to medications or physical therapy | Variable, may lead to long-term pain or instability if the tear doesn’t heal properly |
| Meniscus Repair | Preserves the meniscus, improves long-term knee health, may lead to faster recovery | More invasive, requires more time to heal, may not be successful for all tears | 6-12 weeks | Infection, delayed healing, failure of repair | Good, potentially better long-term outcomes than meniscectomy |
| Meniscectomy | Quick and effective for pain relief, can be performed arthroscopically, less invasive than open surgery | Removes part of the meniscus, can lead to long-term joint degeneration, may not fully address pain or instability | 4-6 weeks | Infection, stiffness, instability | Variable, may lead to osteoarthritis in the future |
Remember, this is just a general overview. It’s essential to consult with a doctor or orthopedic surgeon for a personalized assessment and treatment plan.
Rehabilitation and Recovery Process
Recovering from a torn meniscus requires a structured rehabilitation plan to regain strength, flexibility, and function. The process typically involves several stages, each focusing on specific goals to help you return to your desired activity level.
Stages of Rehabilitation, Torn meniscus recovery
Rehabilitation after a torn meniscus is a gradual process that aims to restore function and minimize the risk of reinjury. It’s typically divided into several stages:
Initial Rest and Protection
This stage focuses on reducing pain and inflammation. You’ll likely need to use crutches or a brace for support and avoid activities that put stress on your knee. Applying ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) can help manage swelling.
Range of Motion Exercises
As the pain and swelling subside, you’ll start gentle range of motion exercises to restore flexibility and reduce stiffness. Examples include:
- Ankle pumps: While lying on your back, lift your injured leg and point your toes up and down.
- Knee extensions: Slowly straighten your injured leg and hold for a few seconds.
- Knee flexions: Bend your injured knee as far as you can without pain.
Strengthening Exercises
Once your range of motion improves, you’ll progress to strengthening exercises to rebuild muscle strength and stability. Examples include:
- Quadriceps strengthening: Sit on a chair and extend your injured leg, then slowly lower it back down.
- Hamstring strengthening: Lie on your stomach and lift your injured leg up, then slowly lower it back down.
- Calf raises: Stand on a slightly elevated surface and raise up onto your toes, then slowly lower back down.
Return to Activity
The final stage involves gradually increasing your activity level, starting with low-impact exercises and progressing to more demanding activities. Examples include:
- Walking: Start with short walks and gradually increase the distance and intensity.
- Swimming: Swimming is a great low-impact exercise that helps strengthen your muscles and improve cardiovascular fitness.
- Cycling: Begin with stationary cycling and gradually progress to outdoor cycling.
Timeline for Recovery
The recovery process for a torn meniscus can vary depending on the severity of the tear, your age, and overall health. Here’s a general timeline:
| Stage | Expected Duration | Milestones |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Rest and Protection | 1-2 weeks | Pain and swelling decrease, able to bear weight with minimal discomfort. |
| Range of Motion Exercises | 2-4 weeks | Full range of motion restored, knee feels less stiff. |
| Strengthening Exercises | 4-6 weeks | Muscles surrounding the knee are stronger, able to perform daily activities without pain. |
| Return to Activity | 6-8 weeks or longer | Able to participate in sports and other activities without limitations. |
“It’s important to note that this is just a general timeline, and your individual recovery may vary. Be patient and follow your physical therapist’s instructions carefully.”
Importance of Personalized Rehabilitation
Every individual’s recovery journey is unique. A personalized rehabilitation plan tailored to your specific needs and goals is crucial for optimal recovery. Working closely with a physical therapist can help you:
- Develop a plan that addresses your individual needs.
- Learn proper exercise techniques to avoid reinjury.
- Progress at a safe and effective pace.
- Receive guidance and support throughout your recovery journey.
Torn meniscus recovery – A torn meniscus can be a painful and debilitating injury, but it’s important to remember that recovery is possible. With the right treatment and rehabilitation plan, you can regain your mobility and get back to doing the things you love.
Learn more about torn meniscus recovery and the steps you can take to achieve a full recovery.
Torn meniscus recovery can be a long and arduous journey, but the dedication of athletes like Justin Jefferson inspires us all. His resilience and determination in the face of adversity are a testament to the power of perseverance. Just as Jefferson has overcome obstacles to become a star wide receiver, those recovering from a torn meniscus can find strength in knowing that their journey, while challenging, is not insurmountable.
